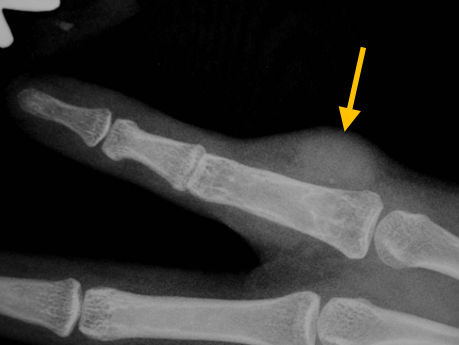
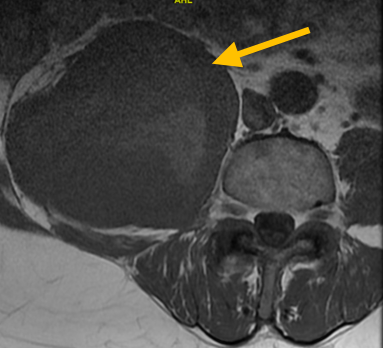
What is a Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans?
Rare type of cancerous skin sarcoma that arises from the dermis of the skin. There is a good prognosis. The 10 year survival rate is 99.1%.
Who is usually affected?
- • Affects patients between 20 to 50 years old.
Common Bones Involved
- • Most common location is around the torso (50%).
Causes
- • Associated with a genetic mutation called a t(17,22) chromosomal translocation. It is a somatic mutation so it does not run in families.
Signs and Symptoms
- • Grows slowly and starts as a flatness in the skin. Usually 1 to 5 cm in diameter.
- • Commonly seen as a reddish or purplish patch of skin.
- • Might look like a pimple or feel like a rough patch of skin.
Biological Behavior
- • Rare type of cancerous skin sarcoma.
- • Arises from the dermis of the skin.
- • Although a skin tumor, the disease tends to grow into surrounding fat and muscle.
- • Slow-growing and rarely spreads, or metastasizes.
Diagnosis
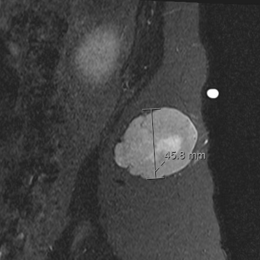
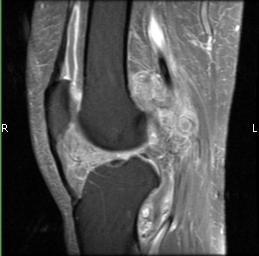
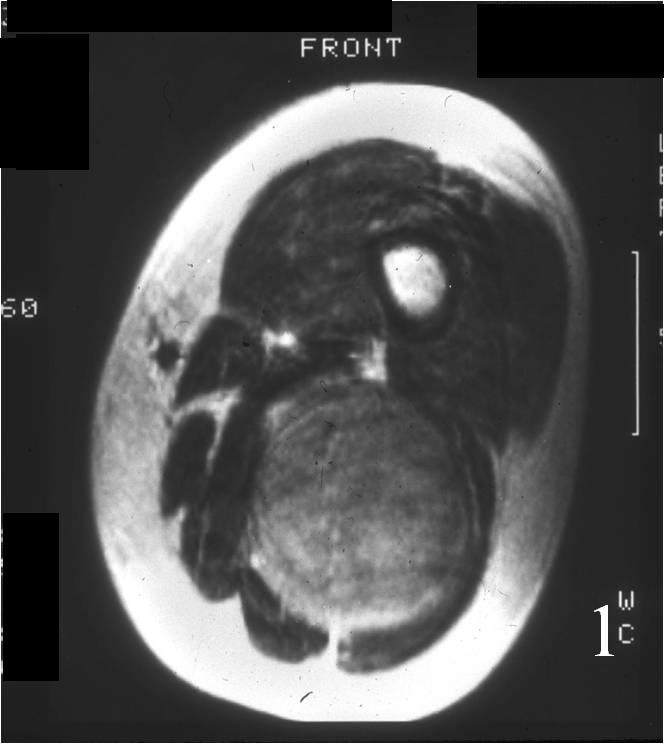
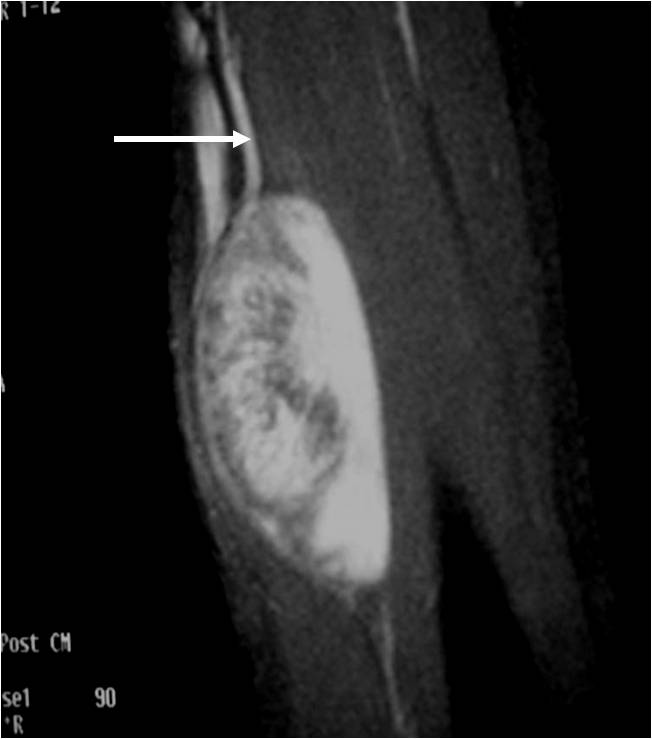
- • The work-up often consists of a physical examination, X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and sometimes bone scans are required.
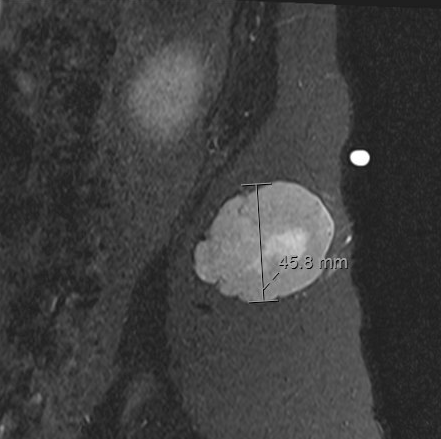
- • MRI is the best imaging because it is the most sensitive.
- • The diagnosis is often confirmed with a biopsy, which means taking a sample of tumor and having it analyzed under a microscope by a pathologist.
Risk to your limbs
Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans is a cancerous aggressive tumor that, if left unchecked, will grow and destroy your normal bone. As the tumor slowly grows, the bone is weakened and you are at an increased risk of breaking the bone due to the tumor (called a pathological fracture). They may also spread to your lungs or other bones.
Radiographic imaging is used to help form a diagnosis. These include X-Ray, MRI, CT and Bone Scans.
An example of a MRI is shown.
Treatment of Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans
Surgery
Mohs surgery is a form of treatment. This procedure is where you remove layers of skin and constantly check for cancer within each layer. Less skin is removed this way. Another treatment is surgical wide resection. There is a tendency for the tumor to recur in the same area after it is surgically removed.
Chemotherapy
is FDA-approved for this condition. Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment option for some cancers, meaning the chemotherapy drugs travel throughout the body and can kill the cancerous cells that have metastasized, or spread throughout. Chemotherapy is used to treat cancer, control/prevent cancer from spreading, and ease the symptoms related to the cancer. There are various drugs used in chemotherapy, so the combinations of drugs administered and the number of cycles may differ between each person and tumor. Lastly, chemotherapy may be used in conjunction with other treatments, specifically local treatments such as surgery.
Radiation
Radiation is a treatment option for some cancers. Radiation therapy is a localized treatment that utilizes high-energy particles or waves to kill cancerous cells. Because radiation therapy is a localized treatment, it only affects the area in which it is set to target and therefore eliminates the risks of damaging healthy cells throughout the body. Not only is it used to treat cancer, but it can also decrease the chances of the cancer from recurring. Lastly, radiation may be used in conjunction with other treatments, such as surgery or chemotherapy, to treat cancers.