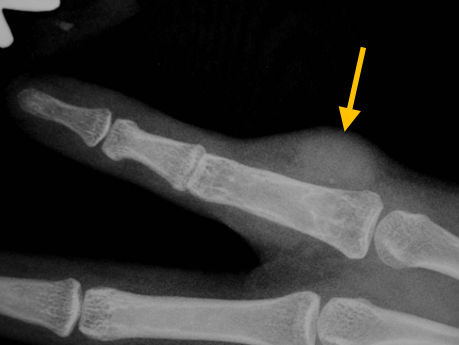
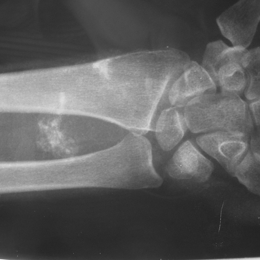
What is Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma of Soft-Tissue?
Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma (UPS) is an aggressive, malignant (cancerous) tumor that most commonly affects the soft-tissues of the upper and lower extremities. Treatment and an early diagnosis are important, as UPS has the ability to metastasize, or spread, throughout the body with the lungs being the most common site for metastasis.
Who is usually affected?
- • The majority of individuals affected tend to belong to the older population.
- • There is also an increased risk if an individual has radiation exposure.
Causes
- • The cause of UPS is unknown.
Common Sites Involved
- • Lower extremities
- • Upper extremities
- • Rarely occurs in the abdomen (retroperitoneum)
- • Can metastasize to lungs, liver, lymph nodes and other bones.
Signs and Symptoms
- • A growing lump or mass
- • Pain
- • Swelling
- • Fever
- • Weight loss
Biological Behavior
- • UPS of soft-tissue originates from mesenchymal cells (stem cells).
Diagnosis
- • The work-up for UPS often consists of a physical examination, X-ray, MRI, CT, and bone scans. Also, a bone scan, CT PET scan, and CT chest/abdomen/pelvis may be ordered to check if the tumor has spread, or metastasized, to the chest/abdomen/ pelvis or other parts of the body. The diagnosis is often confirmed with a biopsy, which samples the tumor for further analysis.
Risk to your limbs
UPS of soft-tissue is a soft-tissue sarcoma. Soft-tissue sarcomas, such as UPS, grow in the soft-tissues of the extremities and compromise or destroy the affected soft-tissue and muscles. These tumors can compress or stretch important vessels and nerves, and occasionally wrap around these structures making it difficult to remove the mass without an amputation. They also have the potential to invade adjacent bones. Without treatment, UPS can metastasize or spread throughout the body, with the lungs, liver, and bones being the most common sites.
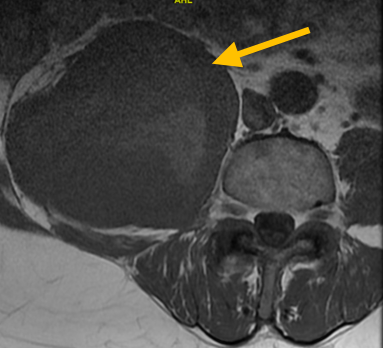
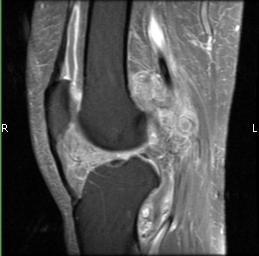
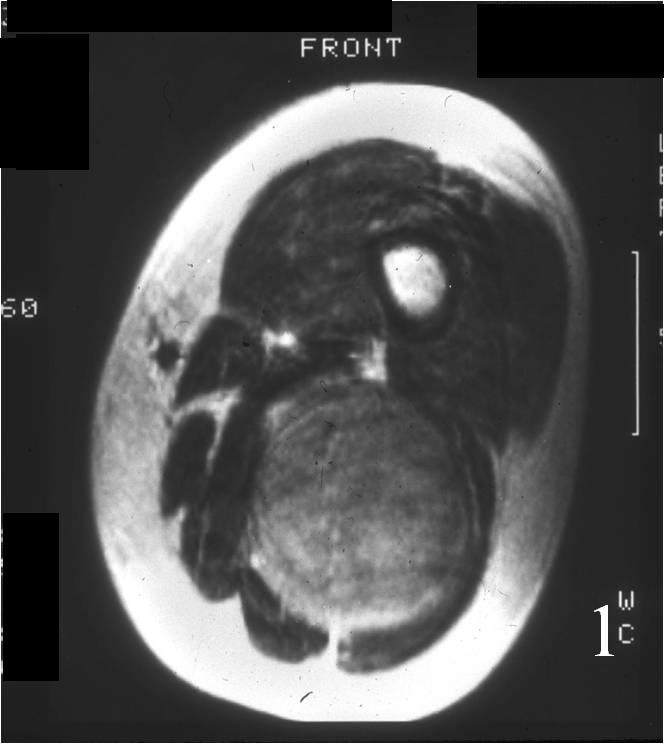
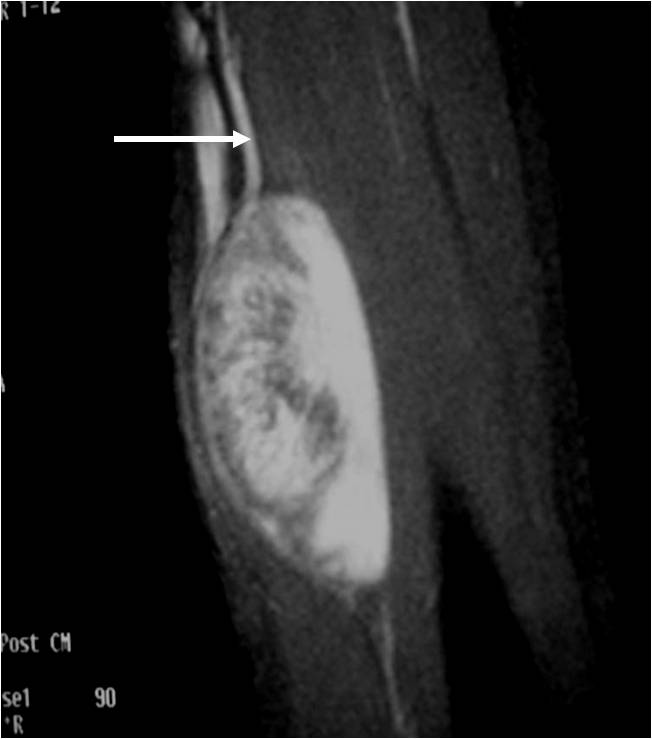
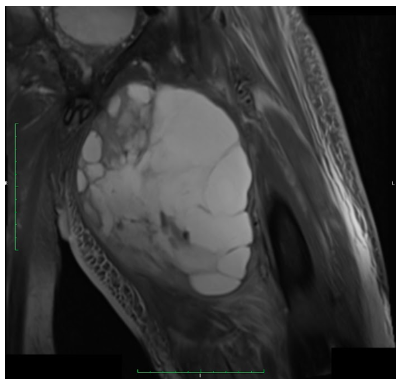
Radiographic imaging is used to help form a diagnosis of UPS. These include X-Ray, MRI, CT and Bone Scans.
An example of an MRI is shown.\
Treatment of Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma
The treatment of UPS includes surgical resection of the tumor through a limb-sparing surgery called a wide or radical resection. When the tumor compresses or stretches important vessels and nerves, or occasionally wraps around these structures, it becomes difficult to remove the mass without an amputation. Additionally, chemotherapy and radiation are used as adjuvant treatments of UPS. Early and effective treatment is essential, as UPS has the potential to metastasize or spread throughout the body, with the lungs, liver, and bones being the most common sites.
Surgery
Surgical treatment includes wide or radical resections to remove the complete tumor and additional margins. The removal of additional, surrounding margins ensures that the tumor is completely removed and decreases the chances of the tumor coming back.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment option for some cancers, meaning the chemotherapy drugs travel throughout the body and can kill the cancerous cells that have metastasized, or spread throughout. Chemotherapy is used to treat cancer, control/prevent cancer from spreading, and ease the symptoms related to the cancer. There are various drugs used in chemotherapy, so the combinations of drugs administered and the number of cycles may differ between each person and tumor. Lastly, chemotherapy may be used in conjunction with other treatments, specifically local treatments such as surgery.
Radiation
Radiation is a treatment option for some cancers. Radiation therapy is a localized treatment that utilizes high-energy particles or waves to kill cancerous cells. Because radiation therapy is a localized treatment, it only affects the area in which it is set to target and therefore eliminates the risks of damaging healthy cells throughout the body. Not only is it used to treat cancer, but it can also decrease the chances of the cancer from recurring. Lastly, radiation may be used in conjunction with other treatments, such as surgery or chemotherapy, to treat cancers.